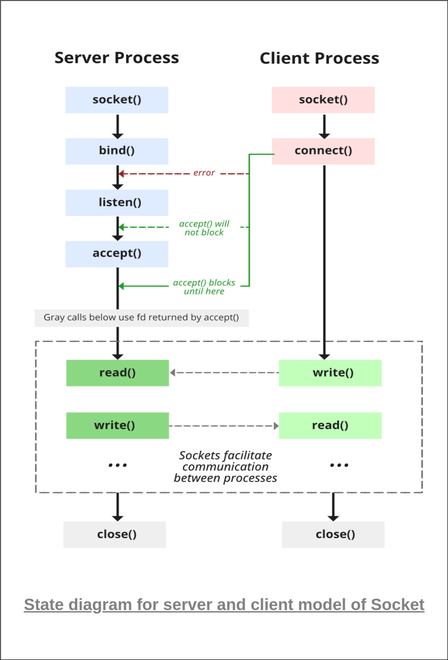
what is socket programming?
Socket programming is a way of connecting two nodes on a network to communicate with each other.
One socket(node) listens on a particular port at an IP, while the other socket reaches out to the other to form a connection.
The server forms the listener socket while the client reaches out to the server.
Socket programming is widely used in instant messaging applications, binary streaming, and document collaborations, online streaming platforms, etc.
Main Functions Provided by <stdio.h>:
| Function | Purpose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
printf() |
Prints formatted output to the console | ||
scanf() |
Reads formatted input from the keyboard | ||
getchar() |
Reads a single character from the keyboard | ||
putchar() |
Writes a single character to the screen | ||
gets() |
Reads a string from the keyboard (unsafe) | ||
puts() |
Writes a string to the screen | ||
fopen() |
Opens a file | ||
fclose() |
Closes a file | ||
fread() |
Reads binary data from a file | ||
fwrite() |
Writes binary data to a file | ||
fprintf() |
Prints formatted output to a file | ||
fscanf() |
Reads formatted input from a file |
stdlib
The purpose of <stdlib.h> (Standard Library Header) in C is to provide functions for general-purpose operations such as:
-
Memory allocation
-
Program control (exit, abort)
-
Conversions (strings to numbers)
-
Random numbers
-
Sorting and searching
🧰 Key Functions in <stdlib.h>:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
malloc() |
Allocates memory dynamically |
calloc() |
Allocates and zero-initializes memory |
realloc() |
Changes size of previously allocated memory |
free() |
Frees dynamically allocated memory |
atoi() |
Converts string to int |
atof() |
Converts string to float (actually returns double) |
atol() |
Converts string to long int |
strtol() |
Converts string to long with base control |
exit() |
Terminates the program with a return status |
abort() |
Abnormally terminates the program |
rand() |
Generates a random number |
srand() |
Seeds the random number generator |
qsort() |
Sorts an array |
bsearch() |
Performs binary search in a sorted array |
🧰 Common Functions in <string.h>:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
strlen() |
Returns the length of a string |
strcpy() |
Copies one string to another |
strncpy() |
Copies up to n characters |
strcat() |
Appends one string to another |
strncat() |
Appends up to n characters |
strcmp() |
Compares two strings |
strncmp() |
Compares up to n characters |
strchr() |
Finds first occurrence of a character in a string |
strrchr() |
Finds last occurrence of a character in a string |
strstr() |
Finds first occurrence of a substring |
memset() |
Sets a block of memory to a specific value |
memcpy() |
Copies memory block |
memcmp() |
Compares memory blocks |
strtok() |
Splits a string into tokens (based on delimiter) |
unistd.h
The purpose of <unistd.h> in C is to provide access to the POSIX (Portable Operating System Interface) API, which includes low-level operating system functions for Unix-like systems such as Linux and macOS.
🧰 Key Functions in <unistd.h>:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
read() |
Reads data from a file descriptor |
write() |
Writes data to a file descriptor |
close() |
Closes a file descriptor |
fork() |
Creates a new process (child process) |
exec() family |
Replaces current process image with a new process |
getpid() |
Gets the current process ID |
getppid() |
Gets the parent process ID |
sleep() |
Suspends execution for a given number of seconds |
usleep() |
Sleeps for given microseconds |
chdir() |
Changes the current working directory |
getcwd() |
Gets the current working directory |
access() |
Checks if the file exists or has the right permissions |
pipe() |
Creates a pipe for inter-process communication (IPC) |
dup(), dup2() |
Duplicates file descriptors |
_exit() |
Terminates the process immediately (used after fork()) |
apra/inet.h
The header file <arpa/inet.h> in C is used for Internet operations, specifically for handling IP addresses and byte-order conversions in network programming on Unix/Linux systems.
🌐 Purpose:
<arpa/inet.h> provides functions to:
-
Convert IP addresses between text and binary formats.
-
Convert data between host byte order and network byte order.
⚠️ It is primarily used in socket programming, especially with IPv4 addresses.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
inet_addr() |
Converts a dotted-decimal IP string to binary (deprecated) |
inet_aton() |
Converts a dotted-decimal IP string to struct in_addr |
inet_ntoa() |
Converts a binary IP address to dotted-decimal string |
inet_pton() |
Converts IP address from text to binary (IPv4 and IPv6) |
inet_ntop() |
Converts IP address from binary to text (IPv4 and IPv6) |
htons() |
Host to network short (16-bit) byte order |
htonl() |
Host to network long (32-bit) byte order |
ntohs() |
Network to host short |
ntohl() |
Network to host long |
netinet/in.h
The header file <netinet/in.h> in C is used in network (socket) programming, and it defines constants, structures, and functions needed for Internet domain addresses, especially IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
⚠️ It's specific to Unix/Linux systems, and part of the POSIX sockets API.
🌐 Purpose of <netinet/in.h>:
It provides:
-
Definitions for address families like
AF_INET,AF_INET6 -
Structures for IP addresses and port numbers
-
Constants for protocols (TCP, UDP)
-
Useful macros for working with network addresses
AF_INET // Address family for IPv4
AF_INET6 // Address family for IPv6
IPPROTO_TCP // TCP protocol
IPPROTO_UDP // UDP protocol
sys/socket.h
The header file <sys/socket.h> in C is used for socket programming. It defines the core socket API, which allows programs to create, configure, and use sockets to communicate over networks.
✅ It is essential for writing any socket-based application in Unix/Linux systems (e.g., TCP, UDP communication).
🎯 Purpose of <sys/socket.h>
It provides:
-
Functions for creating and managing sockets
-
Definitions for socket types and address families
-
Structures and constants used in socket communication
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
socket() |
Creates a new socket |
bind() |
Binds a socket to an IP address and port |
listen() |
Marks a socket as passive (server) |
accept() |
Accepts a connection from a client |
connect() |
Connects a socket to a remote address (client) |
send() / recv() |
Send/receive data through a socket |
sendto() / recvfrom() |
Send/receive data on a socket (for UDP) |
setsockopt() |
Sets socket options |
getsockopt() |
Gets socket options |
shutdown() |
Disables communication on a socket |
close() |
Closes a socket (defined in <unistd.h>) |
| Constant | Meaning |
|---|---|
AF_INET |
Address family for IPv4 |
AF_INET6 |
Address family for IPv6 |
SOCK_STREAM |
TCP (reliable, connection-oriented) |
SOCK_DGRAM |
UDP (unreliable, connectionless) |
SOCK_RAW |
Raw socket (low-level) |